The Wasp Filter uses the somewhat idiosyncratic filter circuitry of the 1978 EDP Wasp synthesizer. The 12 dB filter produces very peculiar, “wild” distortions at higher resonances, which, however, always remain very easy to control. Possibilities and structure of the module (but not the layout of the front panel) are similar to the A-106-5 SEM filter, the sound is of course completely different.
User interface
Inputs:

- Audio In: Audio input.
- CV1: Control voltage input for the cutoff-frequency (without attenuator).
- CV2: Control voltage input for the cutoff-frequency (with attenuator).
Outputs:

- BP Out: Output for bandpass filter mode.
- LP / HP Out: Output for the crossfade lowpass filter / highpass filter (or notch filter) mode.
Controls:

- Lev.: Attenuator for the audio input.
- Frq.: Controller for the cutoff-frequency.
- CV2: Attenuator for the control voltage input “CV2”.
- Res.: Controller for the resonance of the filter.
- Mix: Controller for the filter modes lowpass filter, notch filter (middle) and highpass filter.
Character actor
The filter is well suited for cutting, somewhat distorted solo sounds, for drums and effects. Due to its somewhat unusual sound characteristics, it is less of a “bread & butter” filter, but a very good specialist for more eye-catching sounds with character.
Self-oscillation
If you want a Wasp filter with self-oscillation, you can modify the module (requires a little skill and experience with a soldering iron).
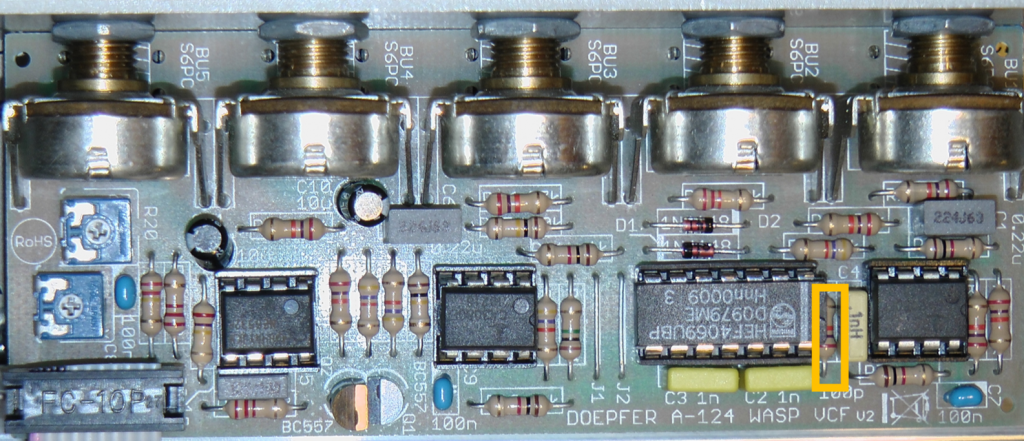
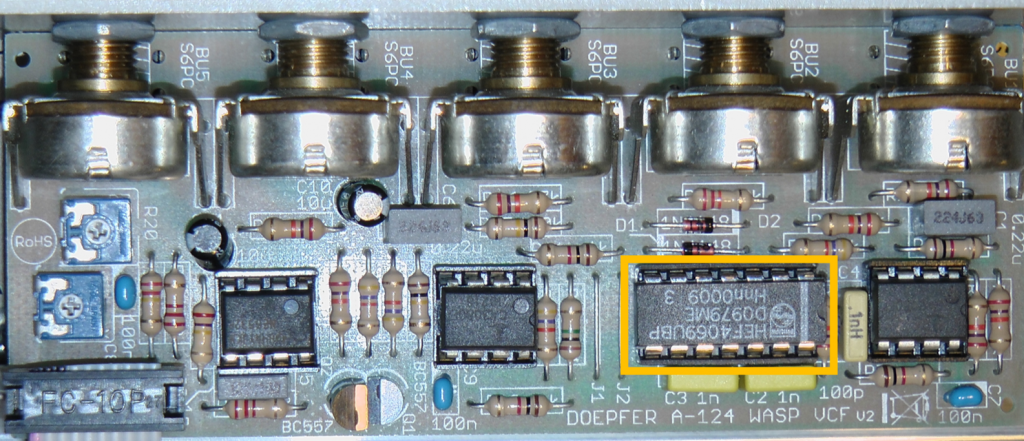
Possible vulnerability
Doepfer pointed out that the built-in inverter module CD4069 can fail in rare cases. Unfortunately, the problem cannot be avoided without removing the filter’s typical “wasp sound”. However, the inverter is a component that is easy to obtain, can be easily replaced and usually costs significantly less than 1 euro. By the way, my own A-124 has been in operation for well over 10 years without any problems…
Sound examples
-
A-124 / Wasp sequence
In this example, the sawtooth outputs of three A-110-1 VCOs are used, with one VCO transposed down an octave. The VCOs are controlled by an A-155 sequencer, the filter is modulated by an ADSR envelope and a slow sine LFO. The input of the filter is set to maximum.
We start without any resonance, I manually fade from lowpass to notch to highpass. Following this, an A-134-1 VC panning/crossfader is used to crossfade from the LP/HP output to the bandpass. Now the resonance of the filter is increased to the maximum. Then we hear the HP/LP output again, I regulate again from the highpass via notch to the lowpass mode and reduce the resonance back to zero.
Wasp sequence.
Technical specifications
| Width | 8 HP |
| Depth | 45 mm |
| Power requirements | 30 mA (+12V) / -10 mA (-12V) |
